Converting Shapefiles (and more) to KML
A while back I wrote about converting KML files into a shapefile for use with GIS apps other than GoogleEarth. I got a ton of emails and site traffic from people looking to go the opposite direction; getting their GIS data into KML.
There are, of course, a couple of utilities already implemented: ArcMap-based extensions including KML Home Companion and Arc2Earth, a nice MapWindow app called Shape2Earth, and the open source WMS Geoserver all support KML output.
Not to be left behind, GDAL/OGR now supports KML output. Oddly enough it does not yet read KML. But hand it any OGR-readable vector dataset and it can be converted into KML. It currently doesn’t offer as much control over the output as the above options but is quicker to implement, works with a wide variety of input formats and can be easily scripted.
This functionality is in CVS only at the moment but should be included in the next release. If you can’t wait and don’t feel like compiling from cvs source, try the 1.0.5 version of FWTools (for Windows and Linux).
The conversion process is pretty straightforward. For example, the following will convert a shapefile (sbpoints.shp) to KML (mypoints.kml).
ogr2ogr -f KML mypoints.kml sbpoints.shp sbpoints
The KML format flys in the face of the GIS mantra stating that content should be seperate from styling. Since styling information is purposefully absent from most standard vector formats, it makes for pretty bland KML output. The attributes just get dumped out into one big text block and there is no classification or styling control.
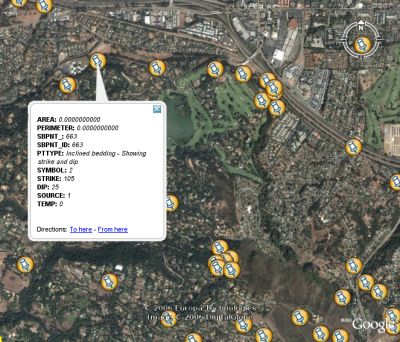
But in terms of getting your data into Google Earth quickly (esp. point data), the OGR method looks promising.
blog comments powered by Disqus
